Climate News

Disaster Risk Reduction and Management has been substantially improved in the town of San Isidro on the island of Samar with the adoption of DRR.Center and flood sensors.

CSS changed its mind about attending the 30th Conference of the Parties and now has feet on the ground in Belem.

Climate Survival Solutions Philippines has completed it first solar irrigation pump installation.

Given the difficulty that nations are having in developing a draft treaty to reduce plastics pollution, Climate Survival Solutions has written a proposed draft treaty and respectfully submits it to delegates for consideration in furthering their task.

Climate Survival Solutions will be presenting an important new policy analysis and transportation roadmap for the future at the 14th Asia-Pacific Conference on Transportation and the Environment. The conference will be held from August 9-11, 2025, in Hanzhou, China.

Our message to the attendees of COP29.

The presentation and exhibition booth of CSS at the UN's 2024 Asia-Pacific Ministerial Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction (APMCDRR) earlier last month resulted in numerous high quality contacts and inquiries.

The first draft of the Sustainable Development & Climate Resilience Plan for the island of Samar, Philippines has been completed.
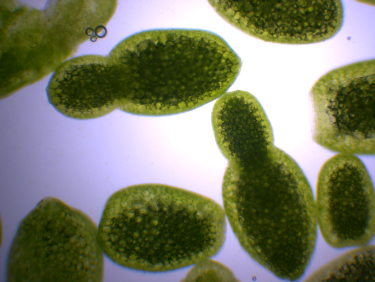
Conventional agricultural fertilizers are a massive problem that Climate Survival Solutions is developing an alternative for.
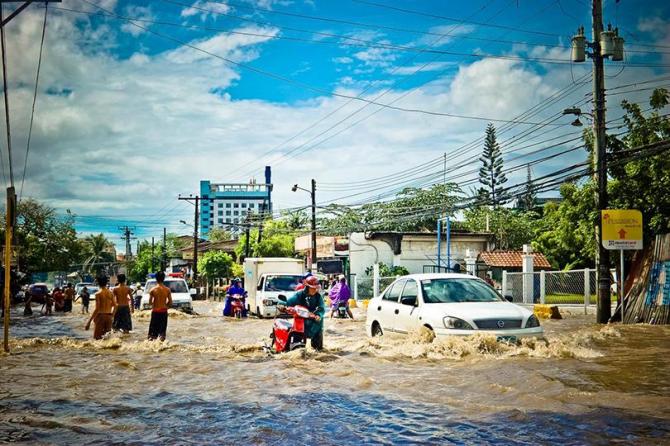

Researchers from Climate Survival Solutions have deployed their new stream level monitoring system to provide early warning of potential floods.

Climate Survival Solutions, Inc., has successfully deployed a prototype small scale hydroelectric power system which can provide backup power for rural communities in the Philippines.

